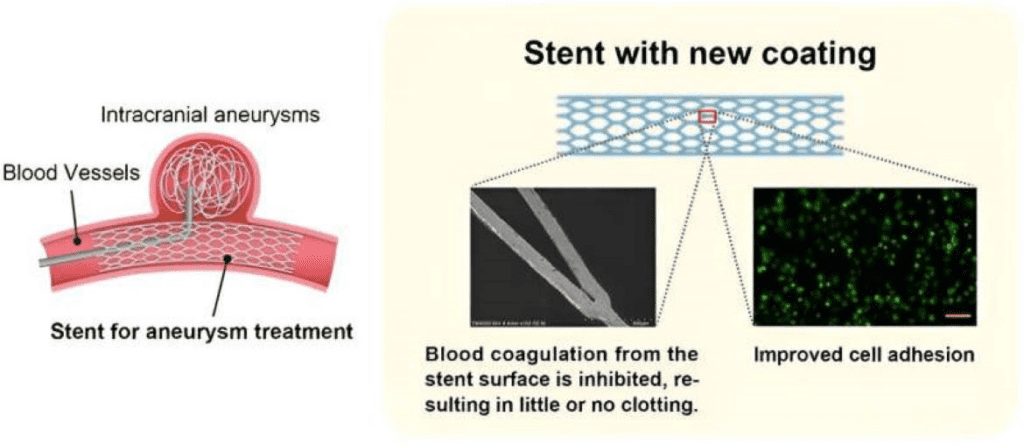
Flow diverters have revolutionized the treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms, offering a minimally invasive solution that helps reduce the risks associated with open surgery. However, the success and safety of these devices hinge on how well their surfaces interact with the body. Advanced surface treatments, particularly specialized coatings, play a vital role in improving the performance and biocompatibility of flow diverters by enhancing their integration with the surrounding vascular tissue and minimizing adverse reactions.
This article examines the importance of coatings for flow diverter, recent advancements in surface treatment, and how Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ coating technology is setting new standards for performance and biocompatibility in neurovascular applications.
The Role of Surface Coatings in Flow Diverters
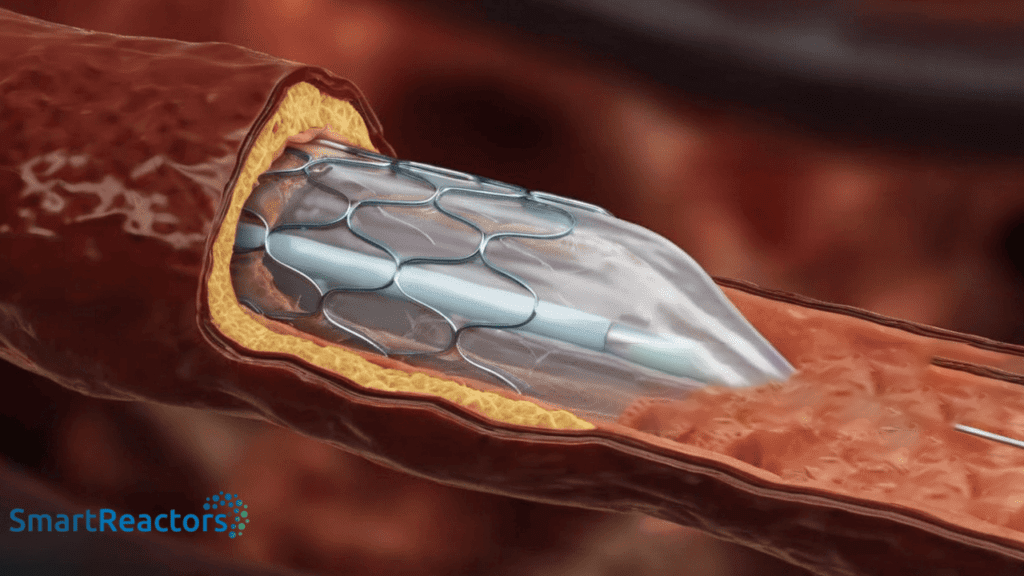
For flow diverters to function effectively within the vascular environment, they must possess a surface that can support healing, prevent thrombosis, and integrate seamlessly with endothelial tissue. Without these features, the device may prompt clot formation, inflammation, or immune reactions, leading to potential complications and reduced device efficacy. Surface coatings are essential to overcome these challenges by enhancing the device’s compatibility and longevity within the body.
Key coating requirements for flow diverters include:
| Thrombogenicity Reduction | Minimizing platelet adhesion to reduce the risk of clot formation |
|---|---|
| Promoting Endothelialization | Supporting the growth of endothelial cells over the device surface to establish a stable, natural vessel lining |
| Reduction in Inflammatory Response | Reducing Inflammatory Response |
| Improving Corrosion Resistance | Preventing ion release from the device surface to enhance biocompatibility and longevity |
These requirements highlight the importance of high-performance coatings for flow diverters in order to maximize device safety and effectiveness in neurovascular applications.
Mr. Brian Haddigan, co-founder of Smart Reactors, emphasizes, “The surface of a flow diverter is the critical interface where engineering meets biology. It’s this nanoscale boundary that determines whether a device will be seamlessly accepted by the body or trigger adverse reactions.”
Innovations in Surface Coating for Flow Diverters
Advancements in surface treatment technology have introduced several key coating techniques that improve the biocompatibility and durability of flow diverters. Among the most effective methods are plasma treatment, ion implantation, and laser surface modification. These methods allow manufacturers to tailor the surface properties of flow diverters, creating a biologically compatible and structurally resilient interface.
1. Plasma Treatment: Plasma treatment is widely used to increase surface energy, which helps to improve cellular adhesion. By creating a nano-textured surface, plasma treatment mimics the natural extracellular matrix (ECM), promoting cell attachment and reducing the risk of thrombosis.
2. Ion Implantation: This process involves bombarding the device’s surface with high-energy ions to modify its atomic composition. Ion implantation enhances corrosion resistance and reduces the release of metal ions (such as nickel), which can cause allergic reactions and hinder long-term biocompatibility.
3. Laser Surface Modification: Laser modification allows for precise control over surface texture, creating micro- and nano-patterns that promote endothelialization. These biomimetic patterns mimic natural cellular structures, encouraging faster cell adhesion and reducing the risk of thrombosis.
Camouflage™: A High-Performance Coating Solution for Flow Diverters
At Smart Reactors, we have developed Camouflage™, a proprietary coating technology designed specifically for blood-contacting devices, including flow diverters. Camouflage™ is a synthetic polymer combined with a proteinaceous base layer that delivers exceptional hemocompatibility, promotes endothelialization and offers long-term stability in the vascular environment. This unique composition allows Camouflage™ to address the primary challenges faced by flow diverters, making it an ideal choice for neurovascular applications.
Camouflage™ technology is particularly effective in:
Providing Long-Term Stability: Camouflage™ is designed for durability and biocompatibility, ensuring a stable and non-toxic surface that withstands the demands of blood-contacting applications. The solid Intellectual Property (IP) backing Camouflage™ further differentiates it in the market, creating lasting value for our customers.
Reducing Clot Formation: By minimizing the initiation of the clotting cascade, Camouflage™ decreases the risk of thrombosis, which is a critical factor in device safety and patient outcomes.
Promoting Endothelialization: The proteinaceous base layer within Camouflage™ supports rapid endothelial cell attachment and growth, helping to establish a stable and natural vessel lining over the device. This feature minimizes the risk of adverse reactions and supports long-term integration.
Mark Brassil, CTO of Smart Reactors, states, “Our Camouflage™ technology integrates multiple advanced surface treatments to create a truly biomimetic interface. We’re not just preventing complications; we’re actively promoting healing and integration at the molecular level.”
Why Camouflage™ is Ideal for Medical Device Manufacturers
For medical device manufacturers focused on neurovascular interventions, Camouflage™ technology provides an advanced, reliable solution that aligns with today’s clinical standards and patient safety requirements. Camouflage™ simplifies the process of producing high-quality, biocompatible flow diverters by offering a multi-functional coating that meets the stringent demands of the neurovascular market. Key benefits of Camouflage™ for manufacturers include:
- Enhanced Biocompatibility: Camouflage™’s non-toxic, hemocompatible composition supports safer implantation, helping to improve clinical outcomes.
- Accelerated Healing: By promoting endothelialization, Camouflage™ enables rapid cell growth over the device, creating a natural barrier that minimizes clotting risk and supports stable vascular integration.
- Long-Term Durability: Engineered to withstand the demands of blood-contacting applications, Camouflage™ provides a reliable coating that enhances device longevity and patient outcomes.
Camouflage™: Setting New Standards in Flow Diverter Coatings
In the evolving landscape of neurovascular devices, advanced surface treatments like Camouflage™ are redefining what’s possible in flow diverter technology. By providing an optimized interface that promotes hemocompatibility, supports endothelialization, and ensures long-term stability, Camouflage™ positions Smart Reactors as a leader in the development of high-performance coatings for medical devices.
For medical device manufacturers seeking to deliver the highest standards of quality and safety, Camouflage™ offers a proven, biomimetic coating solution that enhances the safety and effectiveness of flow diverters, ultimately benefiting both healthcare providers and patients. Through our commitment to innovation and quality, Smart Reactors is helping pave the way for a future where medical devices function seamlessly within the body, improving outcomes and transforming care for patients worldwide.
References:
Chen, Y., et al. (2020). “Surface modification of implantable biomaterials for vascular applications: A review.” Acta Biomaterialia, 108, 1-22.
Maegawa, J., et al. (2019). “Surface modification of neurovascular devices for improved biocompatibility: A systematic review.” Journal of NeuroInterventional Surgery, 11(11), 1047-1052.
Ding, Y., et al. (2018). “Plasma-treated flow diverters: A new frontier in neurovascular intervention.” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 10(25), 21334-21342.
Szikora, I., et al. (2019). “The impact of surface modification on the biocompatibility of flow diverter stents.” Interventional Neuroradiology, 25(3), 279-285.
Food and Drug Administration. (2021). “Neurological Devices; Reclassification of Certain Flow Diverter Devices for the Treatment of Brain Aneurysms.” Federal Register, 86(71), 19785-19792.1
Share this post: on LinkedIn