Carotid artery stenting is a minimally invasive procedure used to restore blood flow in carotid arteries that have become narrowed or blocked due to carotid artery disease—a condition caused by the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaque.
This buildup restricts oxygen-rich blood from reaching the brain, significantly increasing the risk of stroke or other cerebrovascular complications. Left untreated, carotid artery disease can lead to severe neurological damage or even death.
Unlike carotid endarterectomy (CEA), which requires open surgery, carotid artery stenting (CAS) involves the insertion of a self-expanding or balloon-expandable stent to widen the artery and prevent further blockage. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, allowing patients to remain awake and experience a shorter recovery time compared to traditional surgery.
While CAS provides an effective alternative to surgery, stent-related complications such as thrombosis, restenosis, and embolization must be addressed to improve long-term outcomes. Advanced biomaterial coatings, such as Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ coating, enhance stent biocompatibility, reduce clot formation, and promote natural vessel healing.
Understanding Carotid Artery Stents
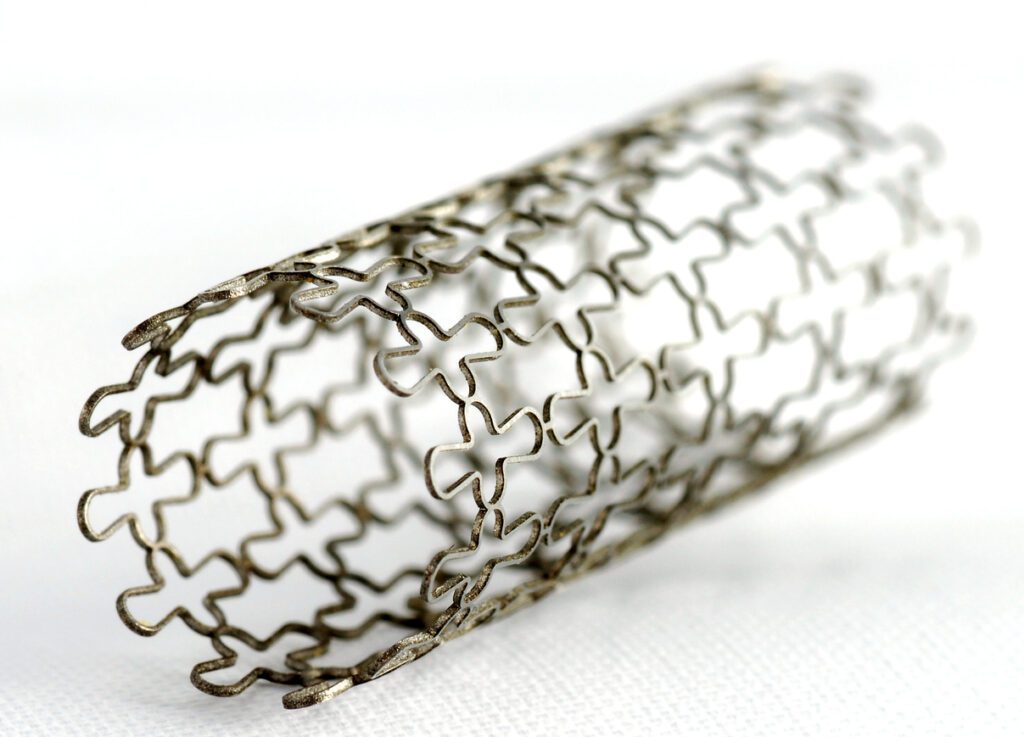
Carotid artery stents are small, mesh-like tubular devices implanted in the carotid arteries to prevent arterial collapse and maintain blood flow. These stents are typically made from self-expanding nitinol or balloon-expandable stainless steel and are often combined with embolic protection devices (EPDs) to reduce stroke risk during the procedure.
How Carotid Artery Stenting Works:
- A catheter is inserted through the femoral or radial artery and guided to the carotid artery.
- A stent is deployed at the site of the blockage, expanding to restore blood flow.
- An embolic protection device captures dislodged plaque fragments to prevent embolization.
- Over time, the stent integrates with the artery as endothelial cells grow over its surface, stabilizing the vessel.
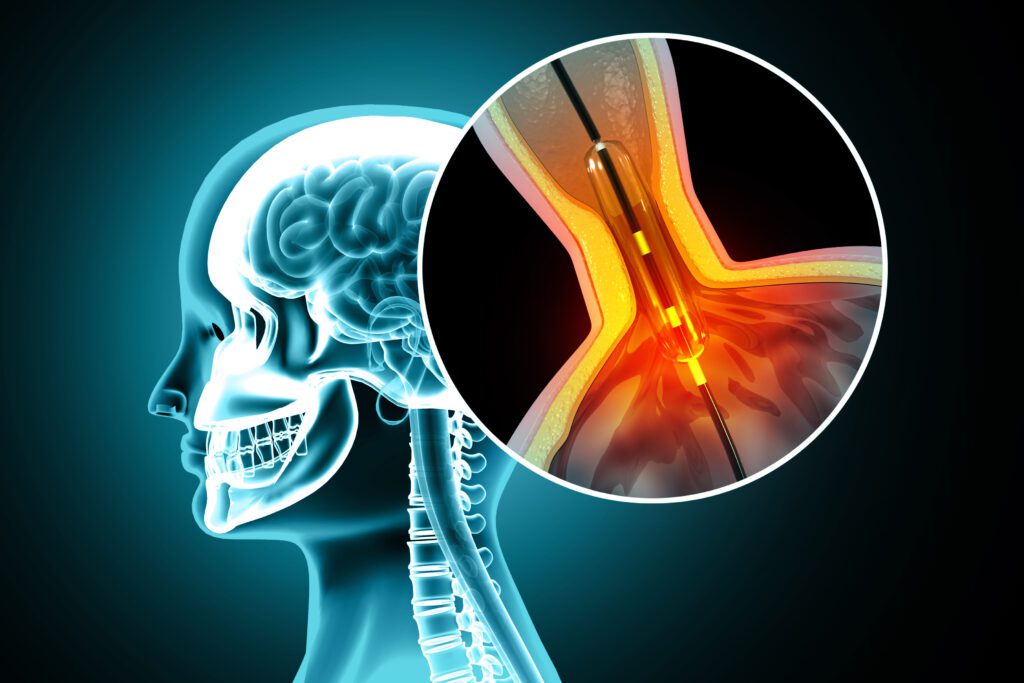
Carotid stenting is particularly beneficial for patients at high surgical risk, including those with severe comorbidities, previous neck surgeries, or high anatomical complexity. However, stent-related risks such as thrombosis, restenosis, and embolization must be carefully managed to improve patient safety.
Challenges in Carotid Artery Stenting
- Thrombosis and Early Stent Occlusion
Exposure to the foreign material of the stent can activate platelets, increasing the risk of clot formation and acute thrombosis. If the stent becomes blocked, blood flow to the brain is compromised, significantly raising the risk of stroke.
- Restenosis Due to Neointimal Hyperplasia
The body’s healing response can lead to excessive smooth muscle cell proliferation, which causes the artery to narrow again, a condition known as in-stent restenosis (ISR). This re-narrowing can require additional interventions.
- Stroke Risk from Embolization
Plaque or thrombus dislodgement during stent deployment can lead to embolic events, where small particles travel to the brain and cause a stroke. Even with embolic protection devices, micro-emboli can bypass filters and enter cerebral circulation.
- Inflammatory Response and Delayed Endothelialization
The body’s immune response to the stent can trigger chronic inflammation, delaying endothelialization and increasing thrombosis and restenosis risks. A well-integrated stent surface is essential for long-term function.
These complications highlight the need for advanced biomaterial coatings that improve stent hemocompatibility, promote rapid healing, and reduce the risk of complications.
How Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ Coating Enhances Carotid Artery Stents
At Smart Reactors, we specialize in advanced biomaterial coating that optimizes vascular implants, including carotid stents. Our Camouflage™ coating is designed to:

- Reduce Thrombosis and Improve Hemocompatibility
Camouflage™ minimizes platelet adhesion and clot formation, preventing early stent occlusion. Its surface properties maintain a smooth blood flow, reducing the risk of ischemic stroke due to clotting.
- Promote Endothelialization and Reduce Restenosis
The coating supports rapid endothelial cell growth, allowing the stent to integrate naturally with the vessel. By limiting smooth muscle proliferation, it also lowers the risk of in-stent restenosis (ISR).
- Lower Stroke Risk by Reducing Embolic Potential
A well-coated stent reduces plaque disruption and the likelihood of embolic particles entering the bloodstream. Camouflage™ helps maintain a low-friction surface, supporting safer CAS procedures.
By integrating Camouflage™ coating, Smart Reactors is helping advance carotid stent technology, making CAS procedures safer and more effective for stroke prevention.
Conclusion
Carotid artery stents are an essential treatment for patients with carotid artery disease, offering a minimally invasive alternative to surgery. However, complications such as thrombosis, restenosis, and embolization can affect stent performance and patient outcomes.
With Smart Reactors’ Camouflage™ coating, carotid stents benefit from improved hemocompatibility, faster endothelialization, reduced inflammation, and enhanced durability. These advancements lead to safer procedures, better long-term outcomes, and lower complication rates.
For medical device manufacturers looking to enhance carotid artery stent technology, Smart Reactors provides cutting-edge coating solutions tailored for vascular implants.
Contact us today to learn how Camouflage™ can optimize carotid stent performance and improve patient safety.
Share this post: on LinkedIn